Temperament and 16 personality types, character traits and personality models

Temperament and personality: these two terms often define what we know and understand about a person and are frequently used interchangeably or in similar contexts. However, there are subtle differences. Temperament refers to how people behave, while personality refers to why people behave in a certain way.
Temperament is more biologically and genetically programmed and inherited. It is not under a person’s control. It manifests in childhood as emotional reactivity and self-regulation ability. Regardless of the temperament type, each type has its positive and negative sides. Parenting and education are aimed at developing the positive aspects of a child’s temperament.
Personality is an acquired phenomenon, shaped by upbringing, education, and experience, and is more under a person’s control. It includes feelings, thoughts, interpretations, and behavior. It is something acquired as compared to temperament and can change over time, for example, with age and interaction.
Primarily, there are 4 types of temperament, as shown below, with their positive and negative traits.
TEMPERAMENT TYPES
| Type | Characteristics | Strengths and weaknesses | Positive and negative sides |
|---|---|---|---|
| Choleric | Decisive and dominant | Leader Goal-Oriented Ambitious Efficient Planning Confident Motivating |
Intolerant Inflexible Impatient Demanding Aggressive Overburdened Stressed |
| Sanguine | Inspiring and influential | Social Communicative Fun-loving Forgiving Optimistic Cheerful, welcoming |
Impulsive Forgetful Selfish, shameless Exaggerative Fickle, hysterical Unpunctual |
| Melancholic | Cautious and conscientious | Thoughtful Organized Self-assured Creative Attentive |
Perfectionist Moody Discontented Pessimistic Anxious Tunnel vision |
| Phlegmatic | Stable and supportive | Calm Balanced Diplomatic Rational Accepting Reliable Consistent Substantial Patient |
Lack of ambition Socially shy Indecisive Permissive Passive Apathetic Compromising |
Below are 4 types of personalities that fully correspond and intersect with the 4 types of temperaments. Thus, it is evident that temperament has a significant influence on the formation of personality. However, personality and its traits depend on the environment, education, and experience.
PERSONALITY TYPES
| Type | Characteristic | Strengths |
|---|---|---|
| A | Director | Risk-taking, goal-oriented, achievement-oriented, competitive,enjoys control, prone to stress |
| B | Socializer | Social, outgoing, relationship-oriented, non-competitive, easygoing |
| C | Thinker | Organized, prepared, logical, detail-oriented, perfectionist, prone to stress and anxiety |
| D | Supportive | Task-oriented, enjoys routine, follows orders, prone to negative emotions, susceptible to depression |
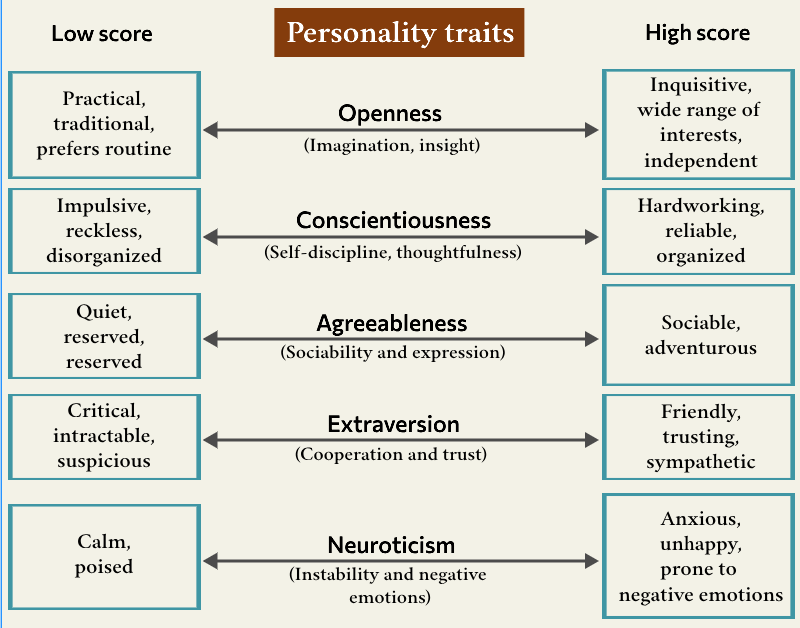
“The Big Five” – personality model
Some psychologists assess personality based on the five major traits depicted in the schematic illustration below.
16 Personality Types
Some psychologists use specific traits to identify 16 personality types based on various permutations and combinations of these traits. The combinations of personality types are derived from eight primary types:
- Extraverts (E). Extraverts draw energy from people, enjoy a variety of tasks, thrive in a fast-paced environment, and excel at multitasking.
- Intuitives (N). Intuitives prefer focusing on possibilities and the big picture, easily identify patterns, appreciate innovation, and seek creative solutions to problems.
- Thinkers (T). Thinkers tend to make decisions using logical analysis, objectively weigh pros and cons, and value honesty, consistency, and justice.
- Judgers (J). Judgers lean towards organization and preparedness, enjoy making and sticking to plans, and find comfort in following most rules.
- Introverts (I). Introverts often prefer working alone or in small groups, favor a more deliberate pace, and enjoy concentrating on one task at a time.
- Sensors (S). These are realistic individuals who focus on facts and details. They apply common sense and past experiences to find practical solutions to problems.
- Feelers (F). Feelers are inclined towards sensitivity and cooperation, make decisions based on their personal values, and consider how their actions will impact others.
- Perceivers (P). Perceivers prefer staying open-ended, enjoy the freedom to act spontaneously, and appreciate flexibility when making plans.

